Atrazine: 7 Harmful Effects On Humans

Atrazine contamination in our water supply is a HUGE concern right now.
And it’s only getting worse.
The question is:
What are atrazine’s effects on humans?
Well, that’s exactly what you’re going to learn in this guide.
Let’s get started.
What Is Atrazine?
Atrazine is an herbicide used to prevent and kill weeds. It also acts as an endocrine disruptor in humans that causes all sorts of deleterious effects.
It’s been over a decade now (2007) since the EPA has recognized this fact:
“studies thus far suggest that atrazine is an endocrine disruptor.”
Atrazine does not occur naturally. It is a white powder that is produced synthetically.
Generally speaking atrazine is used on farms, but it is also commonly used in residential settings on lawns. It’s used for a variety of agricultural purposes:
- macadamia nuts,
- sugarcane,
- corn,
- sorghum,
- pineapples,
- and even Christmas trees.
Is Atrazine Dangerous?
It’s complicated:

Atrazine is one of the most used herbicides in the USA. It’s used so much that it has become the most common pesticide in our drinking water.
That’s not even the worst part.
Atrazine is used in such large quantities and so frequently that it has consistently gotten into our water system at dangerously high levels.
How much atrazine is used in the US annually?
As of 2016 (the most recent data), approximately 70 million pounds.
That wouldn’t be such a big deal, but as it turns out atrazine can have some terrible effects on humans.
Before we dive into the deleterious effects of atrazine, we need to take a minute to understand how we got to a point in history place where we are allowing this chemical to dominate our drinking water.
Confused Frogs, Lawsuits, Hush Money, and Studies Funded by Syngenta
Effects Of Atrazine On Frogs [and Fish]
Here’s a controversial video where Alex Jones makes some comments about how there are chemicals in the water
Is there any truth to his statement?
Let’s take a look.
The study that sparked the controversy was published in a scientific journal called “Environmental Health Perspectives”.
Researchers found that when male tadpoles were exposed to small amounts of atrazine in the water, they ended up turning into hermaphrodites. Said another way, the tadpoles grew up to have both male and female traits. Some of the males even started producing female reproductive cells.

Does atrazine effect other animals like this?
United States Geological Survey scientist Donald Tillitt had this to say:
“Concentrations of atrazine commonly found in agricultural streams and rivers caused reduced reproduction and spawning, as well as tissue abnormalities in laboratory studies with fish”
Here’s the scary part:
He came to this conclusion based on atrazine concentrations that were actually lower than benchmarks set by the EPA.
Lawsuits and Hush Money

Syngenta is the company the produces atrazine.
In 2012 they were the defendant in a class action lawsuit and ended up paying $105,000,000 (That’s 105 million) for over 1000 water filtration systems related to atrazine in the water. After paying this massive amount of money for these systems, Syngenta denied any wrongdoing.
Questionable Research

In 2004, In response to the male frogs turning into females debacle, Syngenta decided to fund a study that attempted to duplicate these findings.
Guess what happened?
The Syngenta funded study failed to reproduce the results of the controversial frog study.
Are we surprised?
In 2013 the EPA responded to the public concern regarding the effects that atrazine might be having on humans. They stated on their website that they would be coming out with a new review of all the available research on it.
Given this significant new body of scientific information as well as the documented presence of atrazine in both drinking water sources and other bodies of water, we determined it appropriate to review the state of the science in light of the new research and to ensure that the agency’s regulatory decisions continue to protect public health and the environment.
Not even one year later in 2014, Syngenta funded their own systemic review of the literature. The authors didn’t find any reason to be concerned:
“the quality of most studies was poor and without good quality data”
So, now we have 2 studies funded by the company that manufactures atrazine claiming that atrazine isn’t a concern.
Am I the only one who finds this concerning?
Atrazine: Effects On Humans
Atrazine can enter the human body a few different ways:
- Orally
- Through the skin
- Through the respiratory tract
Regardless of how it enters a our body, it has been shown time and time again to do all sorts of damage.
How exactly does atrazine effect humans?
Let’s dive right in.
1. Low Testosterone

Atrazine is an endocrine disruptor.
An endocrine disruptor is a chemical or substance that interacts with a humans hormone systems in some way. We know that these interactions can cause all sorts of problems down stream.
There are many ways that atrazine effects our endocrine system, but the big concern for men is that Atrazine reduces luteinizing hormone.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is released by the pituitary gland and ultimately stimulates a mans leydig cells which produce testosterone in the testes.
Long story short, when LH levels are low, so are your testosterone levels.
The bottom line?
Atrazine + human male = decreasing luteinizing hormone = Low T
2. Increased Risk of Miscarriage

Is atrazine linked to miscarriage?
A questionnaire of 2000 farm couples was conducted that had some interesting results:
They found that if the male didn’t wear protective gear during herbicide application the odds ratio (a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome) of spontaneous abortion in his female partner came in at a whopping 5.0 (that’s a lot for an odds ratio).
You read that correctly. The mans exposure to atrazine showed a correlation with the females odds of having a miscarriage.
Which leads us to our next effect on humans:
3. Reduced Male Fertility
Semen quality has long been accepted as one of the primary factors in male fertility.
Atrazine seems to have some nasty effects on seman quality.
In fact:
It has been found to be significantly lower in human males who have metabolites of atrazine in their blood.
4. Low Birth Weight
Atrazine is most heavily applied between May through September.
When a pregnant woman has her 3rd trimester in this time frame, the probability of her giving birth to to a baby that is small for gestational age increased.
We also know that there is also a strong correlation between preterm birth (birth before 37 weeks) and atrazine contamination in the water supply.
5. Increased Chance Of Any Birth Defect
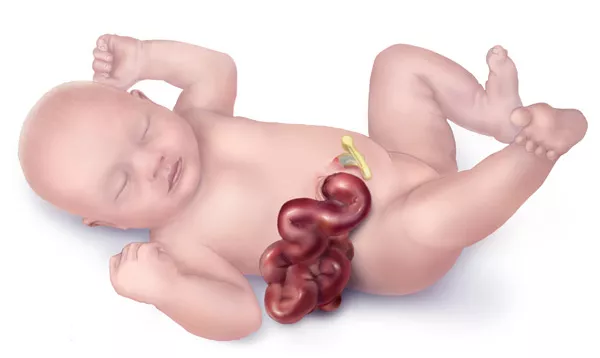
Atrazine has been linked to a variety of birth defects in humans.
Let’s look at a couple.
This is a scary one. Its called choanal atresia. Its when there is extra growth that occurs in the back of the babies airway. It is a life threatening birth defect that requires surgery to correct.
Gastroschisis is another birth defect linked to atrazine.
Gastroschisis is when a child is born with it’s intestines outside of it’s body.
6. Neurotoxicity
It’s no secret that the effects of atrazine are neurotoxic in humans. This neurotoxicity can lead to neurodegenerative disorders.
Specifically:
There is research underway looking into the correlation between Parkinson’s disease and atrazine.
7. Cancer

It shouldn’t come as a surprise that herbicides like atrazine can increase the risk of cancer in humans.
Breast Cancer
Over the past 30 years the US has seen a steady increase in breast cancer.
Studies have found a:
Statistically significant increase in breast cancer risk with medium and high levels of atrazine exposure.
Prostate Cancer
This is probably one of the strongest links seen between atrazine and cancer.
Employees at one of the factories producing atrazine in Louisiana have been found to have rates of prostate cancer 3 times higher than other Louisiana men.
This is crazy:
Prostate cancer rates were highest in men working at the plant who were less than 55. This is interesting because typically prostate cancer rates are higher with increase in age. Not when atrazine is involved.
What Can You Do About It?
There are 3 things you need to consider when it comes to avoiding atrazine.
- Food
- Environment
- Water
What Foods Contain Atrazine?

Buy these foods organic:
- Anything that contains corn
- Macadamia nuts
- Anything with the sugar sucrose in it
- Sorghum
- Pineapple
How can I avoid it in the environment?
If all these effects atrazine has on humans weren’t bad enough, lets briefly talk about our environment.
Why?
It’s important to understand where atrazine levels are highest so that you know whether or not your risk of exposure is high.
Here’s a map showing where atrazine contamination is highest in the USA:
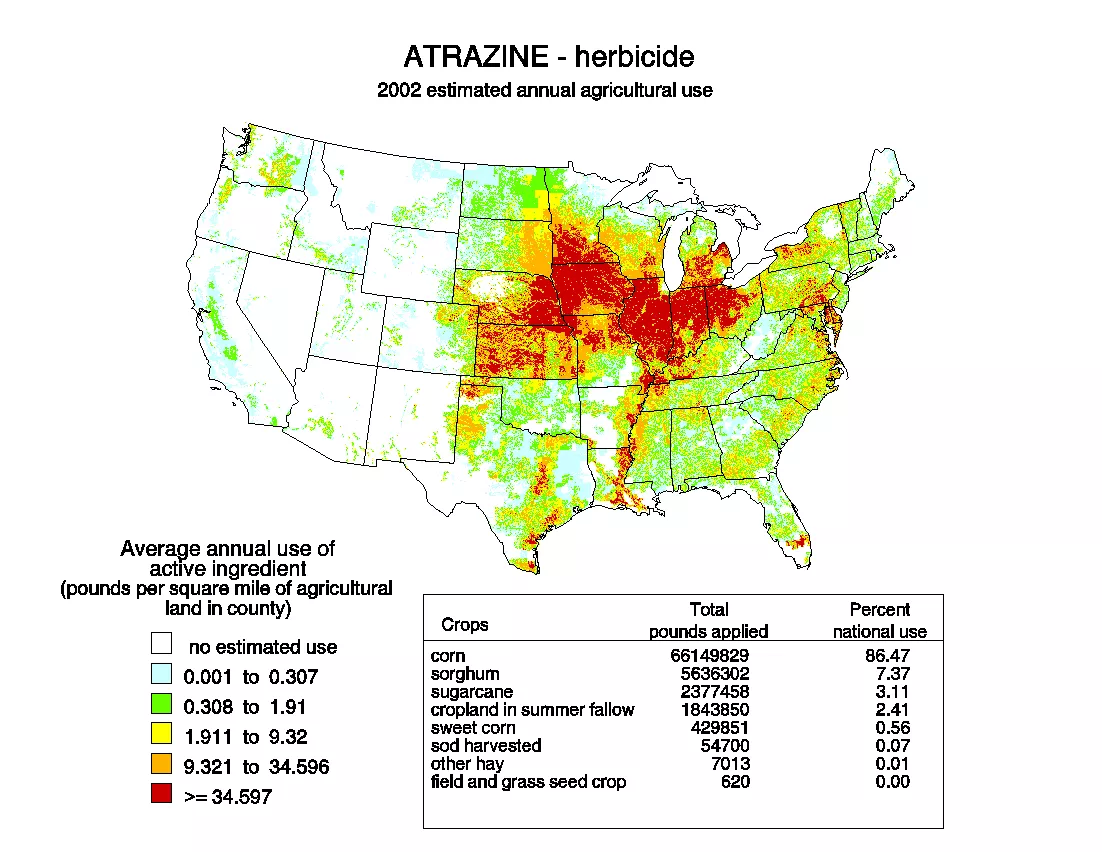
Here’s the interesting part:
After being applied to soil, atrazine can remain in the there for years and years. Eventually it works its way down from the top soil and goes deep into groundwater reservoirs.
Which leads us to our water supply:
Our Water Supply

Have you ever bought a bottle of water that came from a water reservoir that has been “untouched by humans”?
It may not have been touched by humans, but odds are that its been touched by atrazine.
Bottled water is often just tap water from other parts of the country that has been put in a bottle.
Even if you do have a bottle that is atrazine free, its going to cost a ton of money to use that as your only source of water. Not to mention that any brand of water bottle filtering for atrazine is going to cost significantly more than your standard bottle of water.
